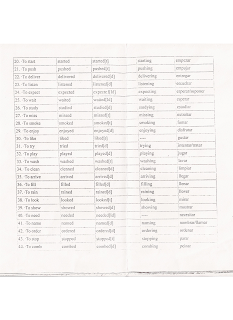
Use of educational activities in the classroom.
It is necessary that in order to develop properly, the process of teaching - learning in the classroom, we put into practice activities that allow students to develop their cognitive process to then make use of the meta cognition. All this is based on the different types of strategy the teacher uses to ensure that students learn and the way in which the students assimilate certain information or knowledge.
The aim of employing various activities in the classroom, allows master captures the attention of students through dynamics to help students learn better knowledge the teacher teach. That is why it is important that the teacher understands how students learn in the classroom, so that in this way find a suitable teaching materials that will benefit the development of skills and abilities of their pupils. But this is necessary to know how to think students and mechanisms to serve as a support to carry out the teaching-learning process.
In such a way, mentioned two important concepts that we should take into account as teachers to analyse them in the classroom and thus enable us to perform certain activities in order that students learn. These concepts are: cognition and Meta cognition.
The cognitive approach, focuses on the mental activity of the student which leads to an answer and recognize mental planning processes. Likewise the cognitivist theories claim that the environment and its components of instruction cannot explain all the learning that results from an instruction. The cognocitivismo is also the construction of knowledge, an individual in particular, in relation to its internal situation and their expectations
Cognitive development is occurring with the reorganization of the cognitive structures as a result of adaptive processes to the environment, based on the assimilation of experience and accommodation of the same with previous knowledge of cognitive structures of apprentices. If the physical or social experience in conflict with previous knowledge, cognitive structures rearrange to incorporate the new experience and what they considered to be learning. The learning content is organized in schemes of knowledge which present different levels of complexity.
Within the cognocitivismo there are various theories that help clarify the process.One of them is the theory of processing the cognitive information that studies the role of the three stages of memory (sensory, short-term and long-term) in the recovery of information and its transfer to store and retrieve memory. Sensory memory enables students to organize groups of information or patterns in their environment, students recognize and process these patterns. Short-term memory allows the student to maintain and understand a small amount of information. If the information is actually linked to prior knowledge, it is stored in long-term memory. Long-term memory allows the student to remember and apply knowledge through learning environments, and remembers the information from a large amount of time once you learn. Encoding and retrieval also play a key role in the theory of the information on cognitive processing (Reiser & Dempsey, 2007).
Existed several thinkers who spoke on cognitive thinking, however one of the most prominent was Piaget which I'll settle a theory in which discovers discover the stages of cognitive development from infancy to adolescence: how psychological structures develop from innate reflexes, are organized during childhood into patterns of behavior, is internalizing during the second year of life as models of thinking, and are developed during childhood and adolescence in complex structures intellectuals that characterize adult life. PIAGET divided the cognitive development into four major periods:
The sensoriomotor (0-2 years), where children start to use the memory, develop a sense of permanence of objects in the intentional activity.
The cognitivista theory emphasizes the acquisition of knowledge and internal mental structures; involved in the conceptualization of the process of the student and are concerned with how the information is received, organized, and stored.
METACOGNItION
Meta cognition is a term used to denote a series of operations, activities, and cognitive functions carried out by a person through an internalized set of intellectual mechanisms that allow you collect, produce and evaluate information, and to make it possible that such a person can know.
That way, you learn to reason about the own reasoning, implementation of the thinking to the Act of thinking, learning to learn, enhance activities and intellectual tasks which one carried out using reflection to guide them and ensure a good implementation.
Both concepts are important in the process of teaching - learning that helps the teacher to understand each student develops and the way in which apply certain knowledge (information to the master da) to daily life.
In conclusion to make use of the classroom activities efficient, we need to consider strategies to help students improve.
In my opinion it is necessary that we as teachers look to the greatest possible number of students so that we know what will be the way to work with the students, some students have a higher level of knowledge than others, and this benefits or harms to the living room, allowing to set new objectives based on the development of skills and abilitiesso we must ensure that students are more beyond what they know so that diverse information to be applied in a practical manner.
jueves, 23 de junio de 2011
martes, 21 de junio de 2011
Practice in "Mariano Matamoros school"
I went to school "Mariano Matamoros" and practiced in 2 ° B. When I started to give the class I first present and told the students the purpose of my class, then gave them sheets containing regular and irregular verbs showing them on the Blackboard some images of verbs, then gave them a text in which students had to identify the structure of the simple past (last vacations) , then explain the structure of the simple past on the Blackboard and I asked them to do a conversation in groups, using the vocabulary of regular and irregular verbs as well as make use of the structure of the simple past, when students finished their conversation went in front of the classroom to say what they had done in their last vacations.
sábado, 18 de junio de 2011
Photos of "Sec. Jorge Murad Macluf"
Introduce myself to the students
Giving and explaining the text
Teh students identify the information that the text contain.
Doing questions to students about the information that I gave.
Students did a conversations relationated with the text.
Students went in front of the classroom to say the conversation
Daily activity
STRUCTURE OF SIMPLE PRESENT
Affirmative: Subject + verb in present + complement
Negative: Subject + do/does + not + verb + complement
Interrogative: Do /does + subject + verb + complement +?
ADVERBS OF FRECUENCY
Para (+) :
Always (siempre)...100%.
Usually (usualmente)...90%.
Often (a menudo)...80%.
Frequently (frecuentemente)...70/60%.
Sometimes (algunas veces, a veces)...50%.
Otras opciones para preguntar:
Ever...? (nunca, jamás, alguna vez...?).
How often...? (que tan seguido o con que frecuencia...?).
Para (-):
Seldom (casi nunca)... 30%.
Rarely (rara vez)... 20%.
Never (nunca)... 0%.
Food & Drink
EXPRESSIONS TO ORDER MEALS
Una mesa para uno por favor
A table for one person, please
Una mesa pra dos, por favor
A table for two people, please
¿Me permite ver el menú por favor?
Can I look at the menu, please?
¿Puedo ver la cocina?
Can I look in the kitchen?
¿Hay especialidad de la casa?
Is there a house speciality?
¿Hay alguna especialidad local?
Is there a local speciality?
Soy vegetarino
I'm a vegetarian
No como puerco
I don't eat pork
Desayuno
Breakfast
Almuerzo
Lunch
Quiero _____ I want _____
Quiero un platillo que contenga ______ I want a dish containing ______
Pollo:Chicken
Carne :Beef
Pescado:Fish
Salmon:Salmon
Atún: Tuna
Bacalao:Cod
Mariscos
Seafood
Langosta:Lobster
Salchicha:Sausage
Queso:Cheese
CONVERSATION TO ORDER MEALS
IN A RESTAURANT
WAITER: CAMARERO
CLIENT: CLIENTE
W: GOOD MORNING, CAN I HELP YOU?
C: YES PLEASE, I'D LIKE A TABLE FOR ONE
W: FOLLOW ME, PLEASE. HERE IS THE MENU
C: THANK YOU. I'D LIKE FOR STARTER A BIG SALAD
W: WHAT WOULD YOU LIKE FOR MAIN COURSE?
C: I'D LIKE FISH & POTATOES, AND FOR DESSERT A BIG APPLE
CAKE
W: WHAT WOULD YOU LIKE TO DRINK?
C: I'D LIKE A WHITE WINE
W: OK., THEN, A BIG SALAD, FISH & POTATOES, A BIG APPLE
CAKE AND A GLASS/ A BOTTLE OF WHITE WINER
************
C: CAN I HAVE THE BILL, PLEASE?
C: OK., HERE YOU ARE, AND THE TIP… GOODBYE
W: THANK YOU VERY MUCH, GOODBYE!
domingo, 12 de junio de 2011
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)